I’m a Ph.D. candidate in Computational and Mathematical Engineering (ICME) at Stanford. I work at the intersection of mechanistic interpretability and AI for science, with a focus on unsupervised methods for scientific data.
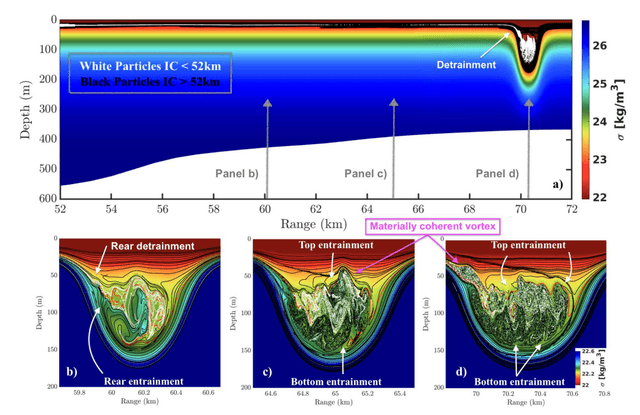
A lot of the problems I care about show up in scientific settings where data are high-dimensional, noisy, and arrive as a stream. Particle physics detectors and accelerator facilities are good examples. I try to build methods that scale on HPC, stay reliable when the data distribution drifts, and are genuinely usable by scientists and operators in the loop.
Current directions
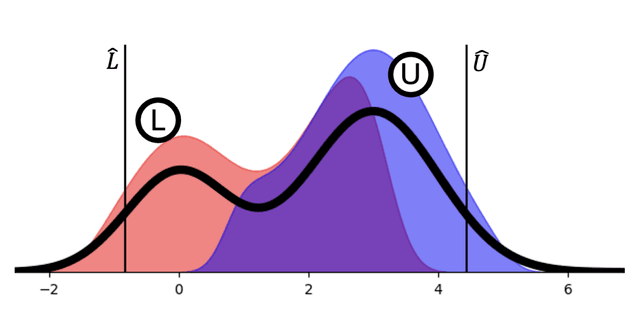
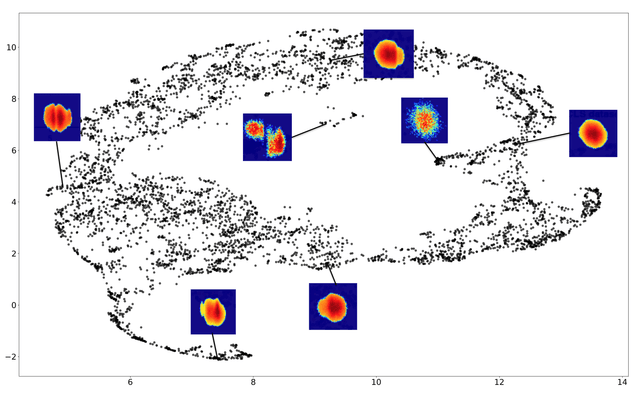
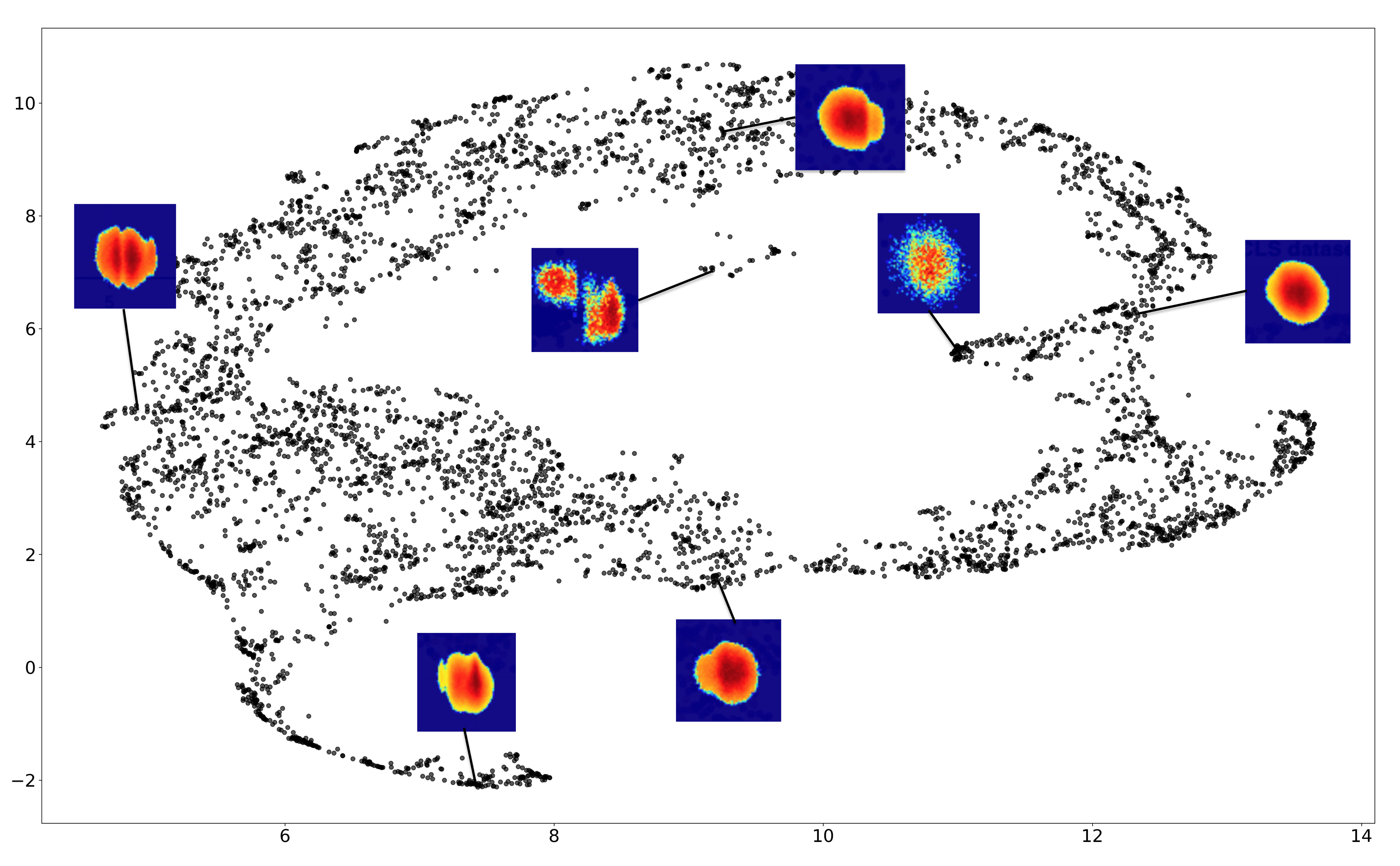
- Mechanistic interpretability: I look for low-rank and block structure in learned representations in order to uncover multi-scale groupings of features and their interactions. Exposing this structure helps clarify how representations are organized internally, while also enabling more efficient and stable training.
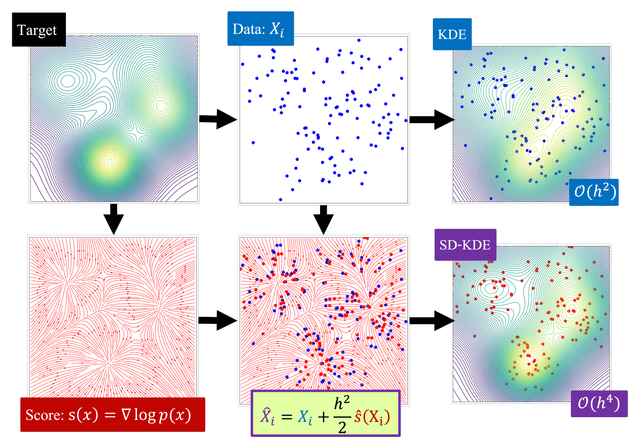
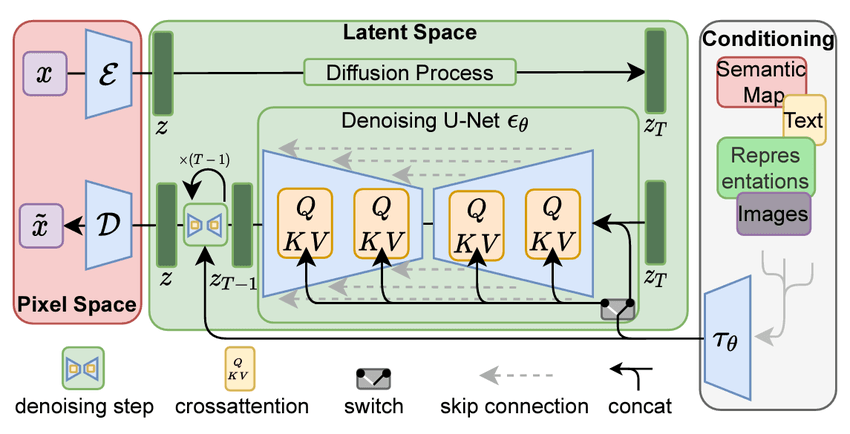
- AI for science: I build modeling and representation-learning tools that fit real experimental pipelines, including probabilistic ideas that help with robustness and uncertainty in messy scientific data.
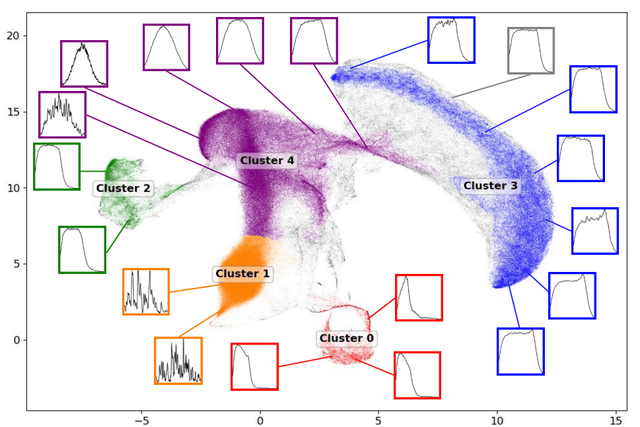
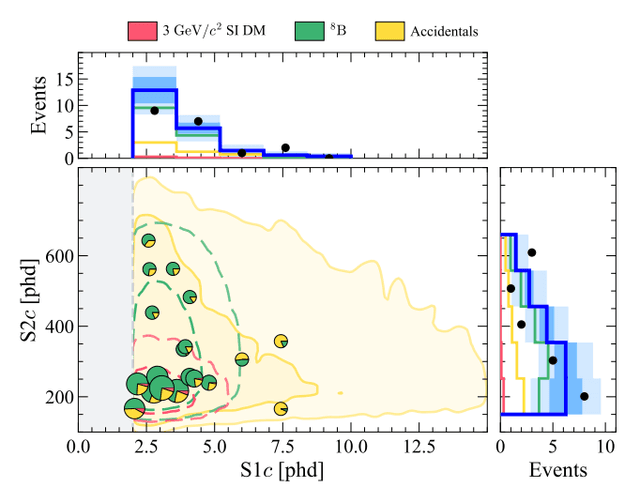
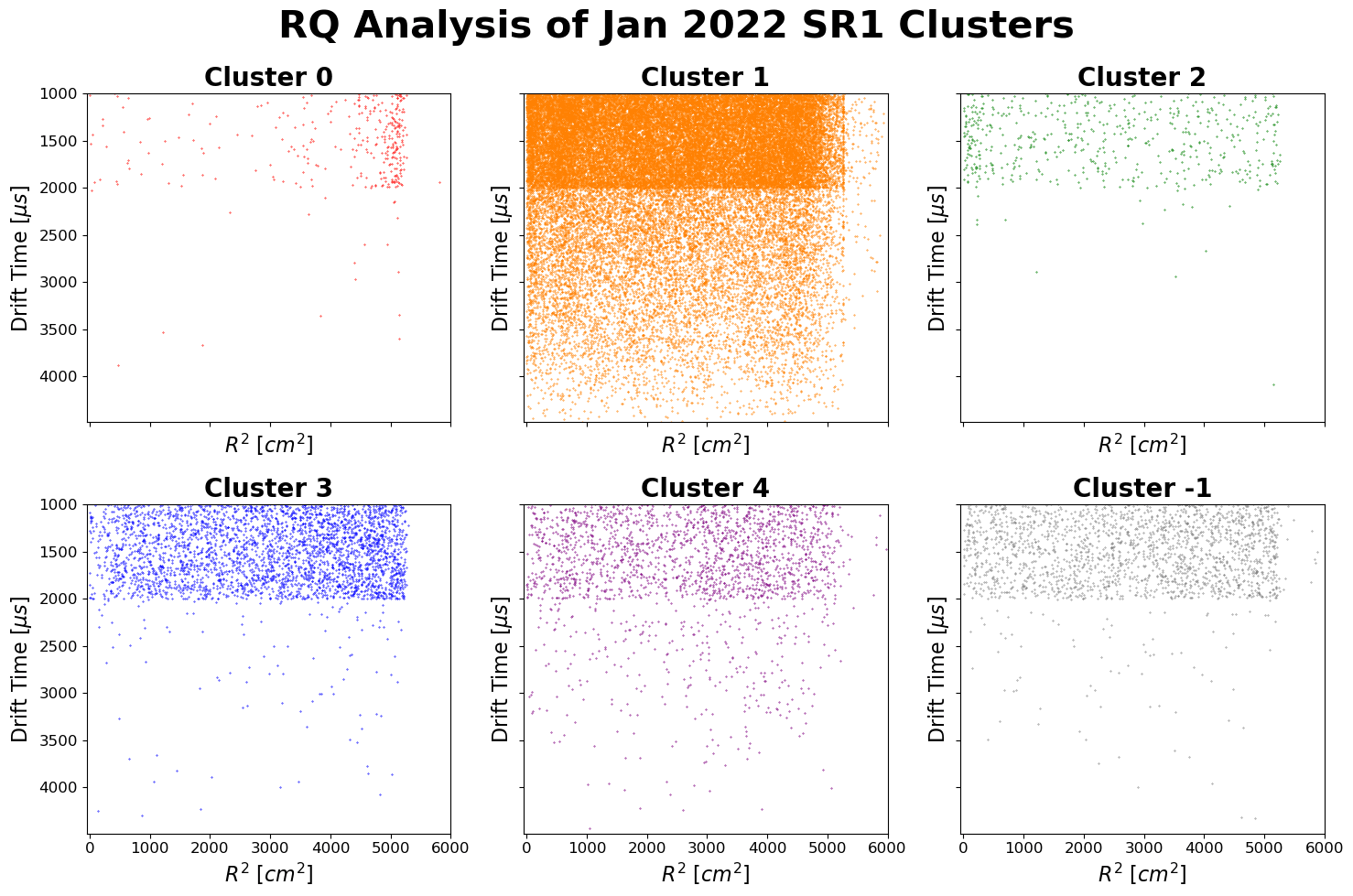
- Anomaly detection: I work on continual-learning anomaly and outlier detection for large-scale physics data, including collaborations with LUX-ZEPLIN and SLAC, with an emphasis on surfacing high-confidence issues while staying stable under drift.
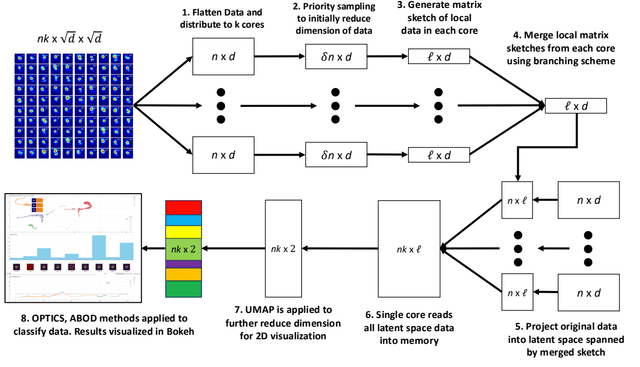
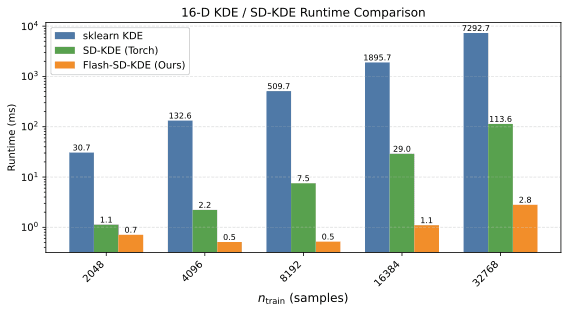
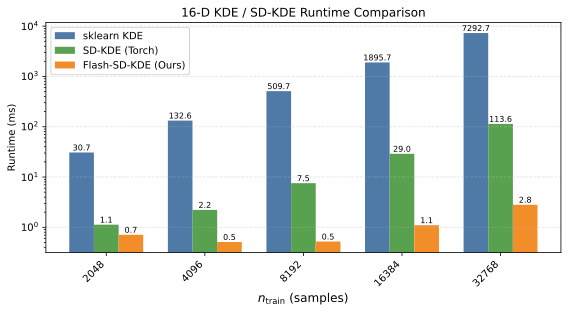
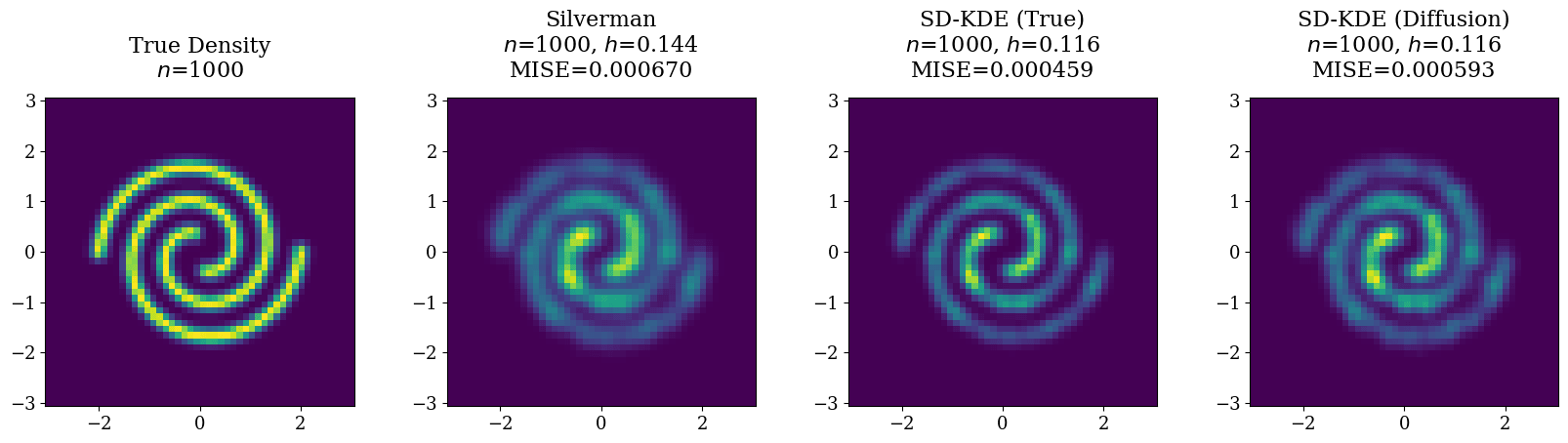
- Unsupervised ML and streaming algorithms: I develop streaming linear algebra and rank-adaptive matrix sketching methods for online analysis, especially for imaging-style datasets, along with practical tooling for monitoring structure and drift over time.